ICSI is a specialized form of IVF treatment commonly used in severe male factor infertility or recurrent failure in fertilisation in conventional IVF. Here a single healthy progressive normal sperm is chosen and micro injected to a healthy egg under the microscope. This microinjection of the sperm to the egg manually brings about the fertilisation of the egg. The fertilised egg is kept in incubators for cleavage and further development of the embryo.
Patients who will benefit from ICSI
When fertilisation in prior IVF cycles failed
Low count of sperms
Abnormal sperms
Low or no motile sperms
For patients with poor ovarian reserve and poor egg quality
Unexplained subfertility
ICSI procedure steps
-
Ovulation induction and follicle tracking
- Induction is done by stimulating the ovaries
- This stimulation is done by administrating hormonal medication such as FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone)
- The female partner’s hormone levels are checked using blood tests
- Simultaneously ultra sound scans are performed to monitor follicular development
-
Oocyte maturation
- HCG injection is administered for the final maturation of the eggs developing in the follicle
-
Oocyte recovery
- Transvaginal ultrasound aspiration is done to retrieve the eggs
- Egg recovery procedure performed under anesthesia
- The aspirated follicle fluid is examined and the mature eggs are separated and placed in culture media and incubated
-
Sperm preparation
- Preparation will separate the immotile and morphologically abnormal sperms
- The final wash will have motile sperms with normal morphology
-
Fertilisation and embryo development
- A high quality motile sperm is taken into the injection pipette (sperm catching)
-
Incubated each egg is taken and injected individually with a selected sperm under the microscope
- The injected egg is incubated and the next day is check for fertilisation
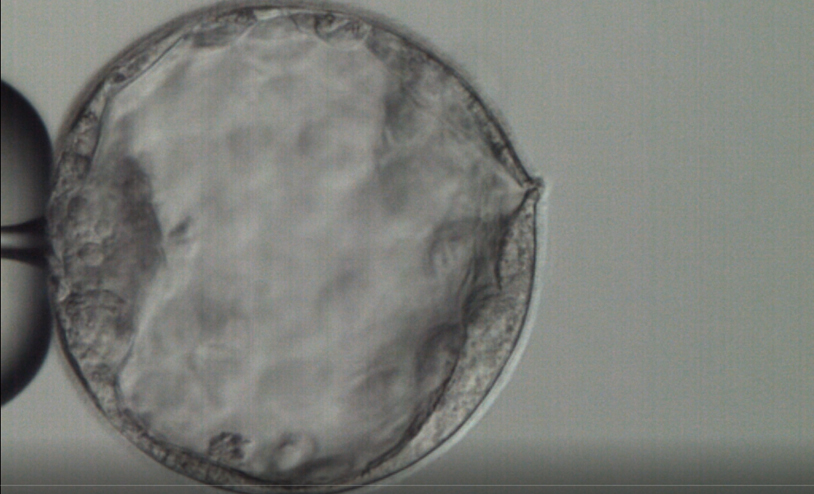
- The fertilised egg develops to an embryo in laboratory conditions
- Embryo development is monitored and then optimally developed cleavage stage (day 3) embryos or blastocyst (day 5) embryos are selected to be transferred and rest is frozen
- Additionally more advanced techniques to assist further embryo development could be used such as, zona thinning and assisted hatching
-
Zona Thinning: Enables the embryos develop further which enhances the ability in implantation in the uterine cavity
-
Assisted Hatching: Enables the blastocyst to herniate which increases the ability in implantation in the uterine cavity
-
Embryo transfer and Serum βhCG test
- Progesterone supplement is given to make the uterine lining ideal for implantation
-
The selected embryos are transferred to the uterine cavity
- After 14 days pregnancy is identified by a βhCG test and further confirmed through an ultra sound scan
