Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI) is a form of treatment, where the washed and prepared sperm sample of the male partner is deposited through the cervix into the uterine cavity of the female partner. The deposited sperm will swim towards egg and fertilise it. The fertilised egg will undergo cleavage; the cleaved embryo will further develop to blastocyst stage and get implanted, resulting with a pregnancy.
Patients who will benefit from IUI
Patients with low sperm counts
Patients with poor sperm motility
Unexplained fertility
Cervical scarring or cervical mucus abnormalities
Vaginismus
Erectile dysfunction
IUI procedure steps
-
Follicular development
- On day 2 of the cycle clomiphene citrate/Letrozole is given until day 6 of the cycle, which helps further development of the follicle
- Leading to the development of a mature egg
-
Tracking the follicle
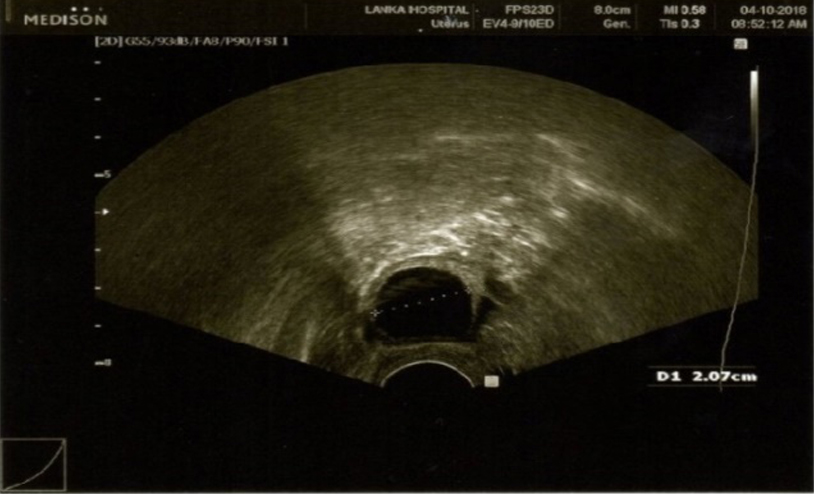
- Ultra sound scanning is done to track the follicle development
- On day 12 another scan is done to see whether the follicle has reached mature state
- HCG injection is given to trigger the release of the egg from the follicle
-
Sperm preparation
- Preparation will separate the immotile and morphologically abnormal sperms
- The final wash will have motile sperms with normal morphology
-
Sperm before preparation
Sperm after preparation
-
Insemination
- Once the egg is released the prepared sperm sample is inseminated to uterus
- The sperms will swim through the fallopian tube and one will fertilise the mature egg
- The fertilised egg will develop to an embryo and will be implanted
-
Serum βhCG test
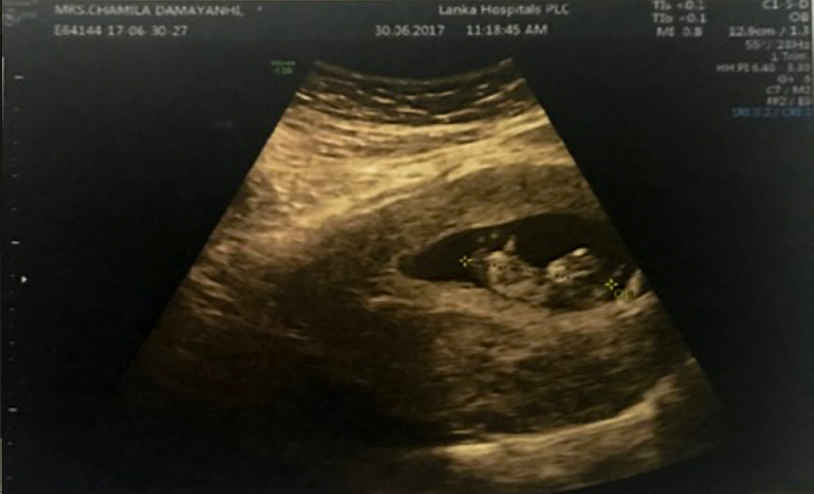
- The implantation of the embryo will lead to a pregnancy which can be identified by checking the levels of serum βhCG and confirmed with an ultrasound scan
